Backup and disaster recovery: Why it’s more than just data protection
Data loss and business disruptions are rising, making backup and disaster recovery (BDR) a critical focus for MSPs. It’s not just about storing data—it’s about ensuring data availability, fast recovery, and business continuity. However, MSPs face growing challenges like fragmented systems, inconsistent processes, and limited scalability.
To overcome these, a strong BDR strategy includes:
-
Data redundancy across multiple locations
-
Continuous backup monitoring
-
Scheduled restore testing
-
Automation of manual tasks
-
Standardized processes across clients
Loss of data can be devastating, not only for the affected organization but also for the MSP responsible for protecting it. These numbers reflect a growing need for MSPs to approach backup and disaster recovery (BDR) as more than a checkbox exercise.
Beyond backups: The true scope of BDR
Backup and disaster recovery is not just about storing copies of data. It involves a strategy that ensures data availability, consistency, and integrity, regardless of unexpected disruptions. This means not only having reliable backups, but also having the systems and processes in place to restore operations quickly when things go wrong.
The challenges MSPs face
As organizations grow and accumulate more data, managing backups across multiple systems, clients, and platforms becomes increasingly complex. MSPs often operate in hybrid environments, using different backup solutions tailored to client needs. This fragmented approach introduces several common challenges:
1. Lack of centralized monitoring
Disparate backup systems make it difficult to monitor backup health at scale. Without a unified view, missed backups or failed jobs can go unnoticed until it’s too late.
2. Inconsistent processes
When backup configurations, testing procedures, and recovery protocols vary across environments, reliability becomes more challenging. Inconsistencies increase the likelihood of failed restores and non-compliance with SLAs.
3. Scalability limitations
Manual backup checks and disjointed processes are difficult to scale. As the client base grows, MSPs must ensure their backup operations can keep pace without compromising service quality.
4. Reactive response times
Without automation and proactive alerting, issues are often discovered after impacting business continuity. This reactive approach contributes to prolonged downtime and potential data loss.
Building a resilient backup and disaster recovery process
An effective BDR plan addresses these challenges through proactive planning, automation, and consistent oversight. A well-rounded strategy should include the following best practices:
Data redundancy
To mitigate risk, backups should be stored in multiple locations. On-premises backups provide speed, while offsite or cloud backups ensure recoverability if local infrastructure is compromised. A hybrid approach enhances resilience.
Continuous backup monitoring
Monitoring is a foundational element of any backup strategy. Automation ensures that failures, missed backups, or anomalies are identified early. This enables swift remediation and reduces the risk of undetected data gaps.
Scheduled restore testing
Backup validity is only proven when data can be restored. Regularly testing data recovery processes ensures backups are present and usable. Establishing a restore testing schedule—monthly or quarterly—enhances confidence and reduces panic during real recovery events.
Automation of manual processes
Automating routine backup tasks eliminates human error and improves efficiency. Teams can shift focus from checking logs to resolving real issues and improving client experiences. Automation reduces time spent on monitoring while improving reliability.
Standardization across clients
Establishing uniform backup protocols across environments reduces complexity and ensures every client receives the same high level of protection. Standardization streamlines onboarding, compliance audits, and disaster response procedures.
The role of backup Monitoring tools
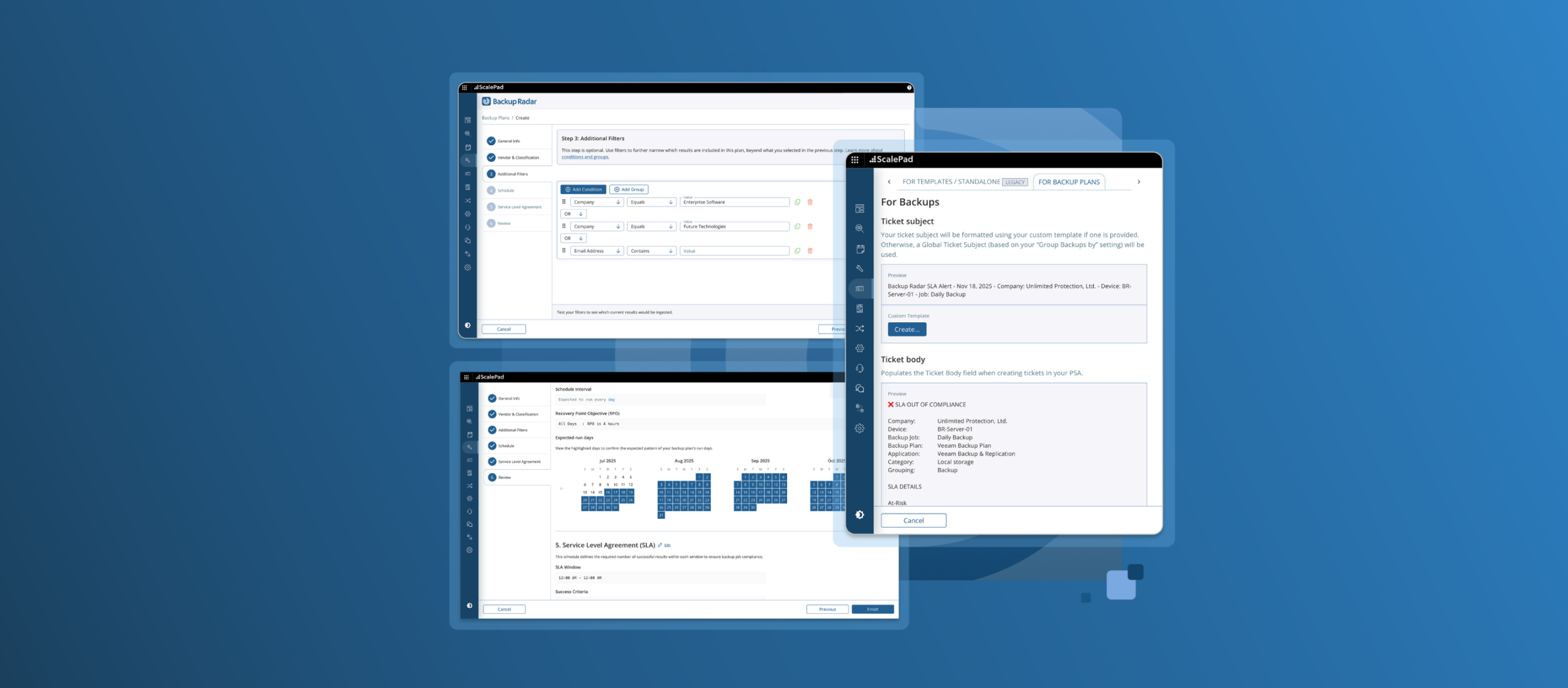
To meet these standards, MSPs often turn to intelligent backup monitoring platforms. One such tool is Backup Radar, designed specifically to help MSPs overcome the operational challenges of backup management.
Key capabilities of backup radar
- Centralized Dashboard: View and manage all backups across clients in a single interface.
- Automation & Alerts: Detect backup issues in real time and notify the right team members.
- Scalability: Support growing data volumes and client accounts without overloading staff.
- Process Standardization: Apply consistent backup rules, testing procedures, and recovery workflows.
- Actionable Insights: Leverage analytics to improve strategies and report on performance.
MSPs using solutions like Backup Radar report improved SLA adherence, reduced time spent on backup checks, and increased client satisfaction. One MSP reduced daily monitoring time from four hours to under an hour, allowing more time to focus on high-impact client work.
Proactive planning prevents crisis
A comprehensive BDR plan prepares organizations to recover quickly from threats such as ransomware, hardware failure, human error, or natural disasters. It ensures the availability of data and the ability to resume operations with minimal disruption.
Every MSP should maintain clear documentation outlining what happens in a disaster scenario, including who does what, how recovery is initiated, and what timelines to expect. This not only brings structure during high-stress situations but also instills confidence in clients.
Backup and disaster recovery as a growth driver
Well-managed BDR isn’t just a defensive measure, it’s a competitive advantage. Clients expect their MSPs to be proactive, reliable, and prepared. Demonstrating consistent backup performance, clear recovery processes, and compliance readiness builds trust and loyalty. That trust leads to stronger relationships, better client retention, and business growth.
Final thoughts
Backup and disaster recovery is far more than an IT routine, it’s a critical business function. For MSPs, it represents both a responsibility and an opportunity. With the right processes, automation tools, and monitoring platforms in place, MSPs can deliver reliable data protection, meet growing client demands, and confidently scale their operations.
Investing in resilient backup management today reduces the risk of catastrophic data loss tomorrow—and helps ensure every client stays protected, no matter what.